Macular Degeneration – Best and Worst Foods
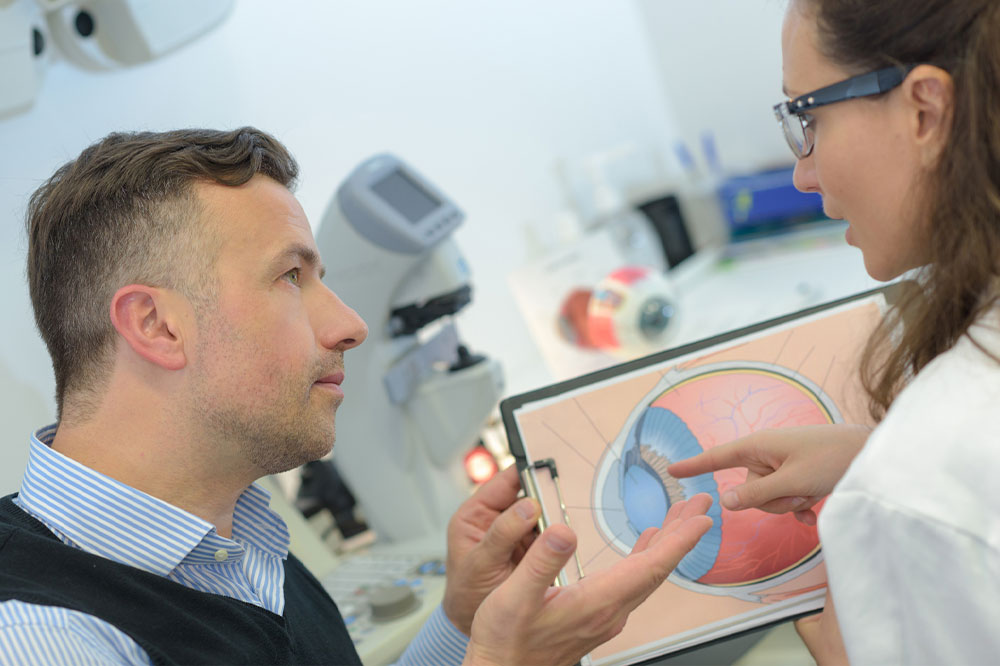
Macula is a small 5-mm portion at the center of the retina. It is located in the back of the eye and is responsible for central and color vision and the fine details of the things we see. Damage to the macula refers to macular degeneration, causing loss of central vision. In most cases, the damage develops over time, usually due to aging. So, the condition is common among people aged 50 and above.
Understanding the condition
Macula is made up of a large number of photoreceptor cells that detect light. Once light enters our eye, these cells signal the brain, which interprets them as images. While age is the most common cause of macular degeneration, family history, diabetes, head injury, eye infection, and nutritional deficiencies are other factors that increase the risk of developing the eye condition. Wet and dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are the two types people experience. With dry AMD, the macular tissue gradually becomes thin and stops working, causing vision loss. Wet AMD results from fluids from blood vessels leaking into the macula. It is a long-lasting disorder leading to blurred vision and blind spots in the central vision. When dealing with eye diseases like macular degeneration, one can experience symptoms like blurry vision, inability to read or notice fine details, blind spots in central vision, and distorted vision.
Cure and prevention
While AMD cannot be prevented, one can prevent regular macular degeneration by treating underlying diseases like diabetes and protecting the eyes from trauma and injury. Some other measures that can prevent or slow down macular degeneration are:
- A meal plan rich in eye-friendly nutrients like lutein, zeaxanthin, zinc, vitamins C and E, omega-3s, and beta-carotene
- Wearing protective eye gear
- Regular and comprehensive eye examinations
- Regulating sugar intake and blood sugar
- Exercising to maintain cardiovascular health and prevent leakage of blood vessels
Food and macular degeneration
There is no specific meal plan that doctors recommend for managing macular degeneration. Unlike in some diseases, where doctors insist on including or avoiding specific foods, there are no strict guidelines for this condition. However, research has shown that by increasing the intake of eye-friendly nutrients like lutein, zeaxanthin, zing, vitamins C and E, omega-3 fatty acids, and beta-carotene, one can delay macular degeneration. Doctors and nutritionists can help one choose the right food and follow a manageable food plan rich in adequate nutrients. Regular and long-term intake of these foods is crucial to prevent macula damage.
Best foods
Lutein-rich food
Lutein is a carotenoid, an organic deep yellow colored-pigment. It is popularly called the eye vitamin, as it is one of the two carotenoids found in the retina. It filters light and protects the eyes from UV radiation when exposed to the sun. The nutrient has anti-inflammatory properties, so adding 10 to 20 mg of lutein-rich food for six months can improve eye health. Some lutein-rich foods are cantaloupe, carrots, corn, egg yolk, fish, orange and yellow pepper, durum wheat pasta, and salmon.
Foods with zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is the second carotenoid in the retina, along with lutein. It helps protect the eyes from the harmful effects of UV radiation and maintains the health of macular tissues. High levels of the nutrient could also help improve visibility in poor light. So, one should choose zeaxanthin-rich foods like asparagus, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, dark leafy greens, green peas, pistachio, pumpkin, Romaine lettuce, and squash.
Sources of beta-carotene
Beta-carotene is a naturally occurring red pigment that gives fruits and vegetables their color. Beta-carotene converts into vitamin A during metabolism, which is crucial for eye health. It is better to add beta-carotene-rich foods to daily meals rather than supplements containing the nutrient, as the wrong dosage can pose health risks. Beta-carotene-rich foods are cantaloupe, carrots, lettuce, red bell peppers, spinach, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, and winter squash.
Fatty fish
The body does not naturally produce omega-3 fatty acids, depending on food for supplying the nutrient. Fatty acids are necessary for cells, tissues, muscles, and nerves to work optimally. Studies show that omega-3-rich food can reverse dry eyes in six to 12 weeks and delay macular degeneration and glaucoma. While cold-water fish like salmon, sardine, mackerel, and tuna are the best options, one can also get omega-3s from fortified food, walnuts, flaxseed, chia seeds, and plant-based oils like canola, soybean, and flaxseed oil.
Foods with zinc
Zinc is crucial for maintaining hormone levels, acid balance, and eye, skin, and hair health. It is also crucial for the immune system. Zinc helps improve vision by mobilizing vitamin A from the liver and delivering it to the eye. Without zinc, the retina may receive less vitamin A leading to macular degeneration. Some zinc-rich foods include chicken, cashew, chickpeas, hemp seeds, lamb, lentils, mushrooms, oysters, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, and yogurt.
Vitamin C-rich food
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that prevents cell damage and fights free radicals. Macula is sensitive to free radicals and oxidative stress, so foods with vitamin C can help prevent damage to the macula’s photoreceptor cells and deactivate the free radicals. The vitamin can also fight any inflammation in the macula. It works best when combined with other eye-friendly nutrients. Good sources of vitamin C are bell peppers, blackcurrants, broccoli, broccoli, gooseberry, kiwi, leafy green vegetables, oranges, and strawberries.
Vitamin E
Alpha-tocopherol is a powerful form of vitamin E and an antioxidant. It can protect parts of the eyes, like the retina and the lens, which are susceptible to oxidative stress. So, one can choose foods like almonds, avocado, beet and beet greens, hazelnuts, kiwis, mangoes, peanut and peanut butter, sunflower seeds, and wheat germ oil.
Worst foods
Foods that clog the blood vessels and cause fluids to leak into the macula can worsen disease symptoms. So, one should avoid foods high in sugar, and transfats, as they can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of macular degeneration. Some such foods are fatty meat like beef, pork, and lamb, processed foods like packaged chips and sweets, rich dairy products, sugary sweets, carbonated beverages, and vegetable shortening.

