Hyperglycemia – Causes, symptoms, and management
According to experts, nearly 28.7 million people live with diabetes in the country. These statistics indicate the need to manage high blood sugar levels to keep this condition at bay. High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, contributes to several conditions like diabetes or kidney diseases. However, one can prevent or delay such complications by following healthy lifestyle habits and monitoring blood sugar levels. Read on to learn about hyperglycemia, its causes, symptoms, and management.
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition that results from glucose concentration in the blood. Glucose is the body’s primary energy-providing source, which comes from the food you eat. On the other hand, insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, responsible for releasing glucose as needed into the bloodstream to carry out day-to-day activities. The blood glucose level might fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors, including your physical activity and the food you eat. When the insulin level is too low, the cells cannot receive adequate energy for normal functioning. The lack of energy will force the pancreatic cells to secrete more insulin, which the body cannot use. It will, in turn, increase the glucose concentration in your blood, leading to hyperglycemia.
Symptoms
High blood sugar is associated with severe health ailments, including skin problems, dental diseases, heart problems, and neuropathy. However, people usually don’t notice the symptoms of hyperglycemia until the blood sugar levels spike too high. Some common early warning signs and symptoms to look out for include the following-
- Blurred vision
- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Headache
- Persistent fatigue
- Fruit-smelling breath
- Abdominal pain
- Sudden or unexpected body mass loss
- Irregular breathing
- Nausea/vomiting
- Warm or dry skin
- Delayed healing of wounds
- Recurrence of yeast infections
Causes
Excessive carbohydrates intake
Many food groups, even healthy options like veggies and fruits, can increase your blood sugar level when you eat beyond the recommended amounts. Additionally, unhealthy eating habits and excessive carb intake may lead to insulin overproduction in the body, resulting in hyperglycemia. For example, if your nutritional plan recommends 60 grams of carbs, but you eat 90 grams, insulin resistance will lead to high blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance
Individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus tend to experience insulin resistance. The blood sugar levels become too high, usually due to the inability of the pancreas to generate adequate insulin or the body’s inability to process the secreted insulin properly. Thus, even though the body still secretes insulin, it may not recognize and process the hormone effectively. Therefore, the excess insulin will be accumulated in the bloodstream, failing to bring glucose energy to the cells. It, in turn, leads to excessive blood sugar.
Unhealthy exercise regime
A poor exercise routine or an inactive lifestyle can negatively influence the insulin level in your body. It will, in turn, lead to the accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream. However, engaging in strenuous activities while dealing with high blood sugar may also result in hyperglycemia. Research suggests that increased physical activity will stimulate the body to release the adrenaline hormone, increasing the blood sugar level.
Illness or stress
Consistent mental stress contributes heavily to high glucose levels. Physical stress caused by injury or illness like cold or flu may also lead to hyperglycemia. When stressed, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline that signal the pancreas to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. It increases blood sugar levels, which can be damaging if it happens too frequently or becomes chronic over time.
Irregular sleep pattern
Not getting enough sleep affects not only your mood but also the ability of your body to break down blood sugar. Irregular sleep regimens (inadequate sleep hours or oversleeping) signal your body to use insulin less efficiently, increasing blood sugar above the healthy range.
Prescription
If you have hyperglycemia, your healthcare professional may prescribe insulin doses to lower your blood sugar levels. However, missing or overdosing on insulin might cause the sugar level to spike. Similarly, other prescriptions like corticosteroids or diuretics may also increase your blood sugar.
Diagnosis
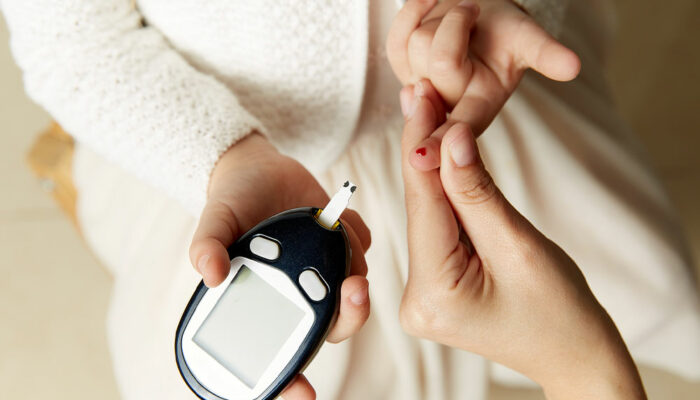
Monitoring your blood sugar at home with a blood glucose meter is one of the simplest and most effective ways to diagnose hyperglycemia. The ideal blood sugar level should be between 80 and 130 mg/dL for people under 59. A number higher than 130 would imply excessive blood sugar.
Remedies
High blood sugar can be tricky to diagnose and manage, but with self-monitoring and early diagnosis, it is possible to reduce the risks effectively. Taking prompt action at signs of this condition could produce significant positive outcomes for your well-being in the long run. The steps listed below will help you better manage hyperglycemia.
Nutritional changes
A meal plan rich in non-starchy vegetables, legumes, and whole grains is recommended, as well as limiting the amount of saturated fat (in refined oils and cheese) taken in. Additionally, eating several small meals throughout the day instead of three large ones can help manage high blood sugar levels more effectively.
Physical activity
Activities like walking, cycling, swimming and running are great low-impact options that can reduce stress while increasing your body’s sensitivity to insulin. In addition, it helps the body to process blood sugar more efficiently.
Consult a health professional
Ensure you take the prescribed treatment and regularly track your blood sugar level. With the recorded blood glucose value, follow up with your healthcare professional to determine if they want to change the prescribed doses.
Hyperglycemia is a potentially severe health issue that could lead to long-term complications if not monitored and managed correctly. The primary cause of this condition is an imbalance between insulin and glucose levels, often due to diabetes. One can manage the condition through lifestyle changes, such as following a balanced meal plan and being more physically active. In addition, it is advised to consult a nutritional expert regarding any queries about hyperglycemia to chart out the best treatment option.

