Atopic dermatitis management in children
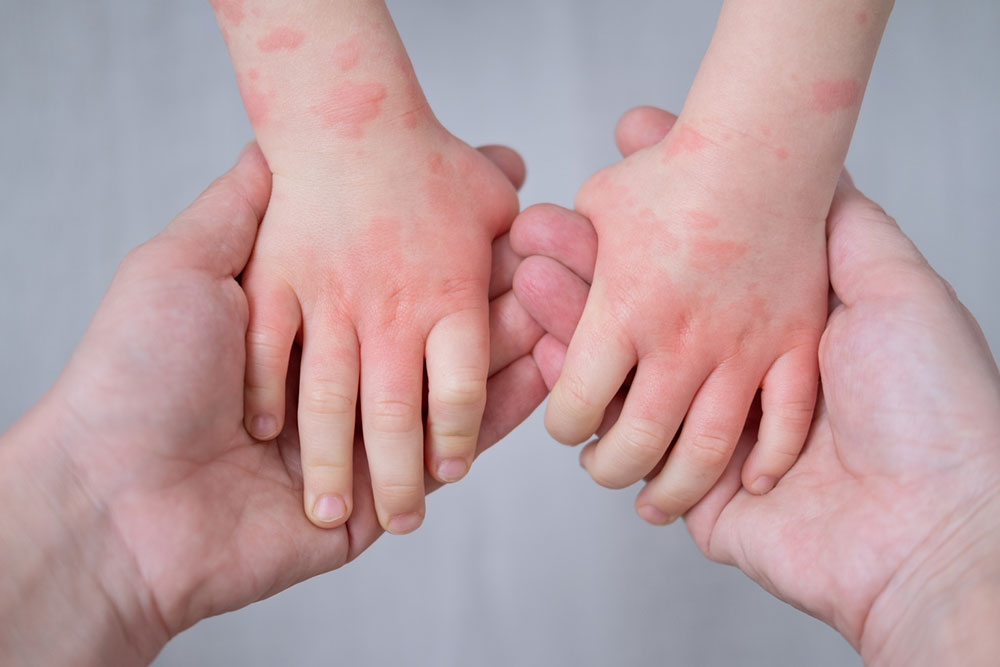
Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by skin inflammation and irritation. The condition can affect people of all ages, including children, so parents should keep an eye on some of the symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, from one child to the next. Once the signs are identified, parents or guardians could start the child on the treatment options mentioned below to help manage the condition.
Signs of atopic dermatitis
Before getting into the treatments for atopic dermatitis, parents and guardians need to know about the signs. This could help identify, diagnose, and manage the condition immediately. The symptoms may come and go or occur most or all of the time. One should also note that any region of the child’s body might be affected. Babies usually develop atopic dermatitis in the face, skin inside the elbows, back of the knees, side of the neck, scalp, hands, wrist, and around the mouth. The symptoms may vary for each child. These include the following:
- Dry, scaly skin
- Pale skin on the face
- Redness and swelling
- Darkened skin of the eyelids or around the eyes
- Rough bumps on the face, thighs, and upper arms
- Severe itching
- Skin that turns thick
- Small, raised bumps that might turn crusty and leak fluid if scratched.
- Skin changes around the mouth, eyes, or ears
- Raised, red areas (hives)
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis could be like those of other health conditions. Therefore, one should ensure they check with a specialist to determine the source of the development.
Causes
Experts believe there are multiple factors linked to the occurrence of atopic dermatitis in children. Some of these are as follows:
- The condition might be passed down from parent to child.
- An immune system that isn’t fully developed might affect the amount of resistance the skin gives when affected by atopic dermatitis.
- External factors like winter weather, using hot water for bathing, strong soap, and being in hot, dry temperatures might also influence the condition.
Treatment options for atopic dermatitis in children
The treatments for atopic dermatitis may vary based on multiple factors. These include the child’s symptoms, age, and general health. An expert may also recommend treatments based on the severity of the condition. A cure for atopic dermatitis is still to be identified. Meanwhile, healthcare professionals aim to ease inflammation and itching and add moisture to prevent and improve complications. A few treatment options include the following:
1. Emollient
One of the first-line treatments for atopic dermatitis in children is cream and ointment. These are applied directly to the skin’s surface to ease itching and swelling. They work by reducing water loss and covering it with a protective film. Emollients are usually prescribed to children with atopic dermatitis who have symptoms like dry or scaly skin. These may also help make the skin less dry and reduce the number of flare-ups one has. Various types of emollients are available, so one should speak to an expert about the type that would work for the child. Doctors may also ask parents or guardians to use a mix of emollients for the child’s skin, such as the following:
- Ointments for extremely dry skin
- Emollients to use instead of soap
- Cream or location for red, inflamed skin
- Specific emollients to use on the face and hands
Lotions, ointments, and creams can be differentiated based on how much oil they contain. Ointments contain the most amount of oil and are quite greasy, but they are super effective at keeping moisture in the skin. Lotions contain the least oil and are usually not very effective. And creams usually have an in-between level of oil concentration.
2. Phototherapy
This therapy is indicated for children who do not get better with topical treatments or rapidly flare again after treatment. The simplest form of light therapy involves exposing the affected area to controlled amounts of natural sunlight. Other forms use artificial ultraviolet A (UVA) and narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) alone or with other treatment options. While long-term therapy is effective, it may have side effects that parents should speak about with the expert. It is also why the method is less common in children and not given to infants.
Other management methods
Apart from treatments, an expert may also recommend management methods to prevent symptoms like inflammation caused by atopic dermatitis.
- Bathe frequently
Children with atopic dermatitis must bathe frequently and use moisturizers. Parents should also ensure that the child has a bath over a shower. Adults must also ensure that their kids use mild soaps and limit their usage of the product. - Maintain short fingernails
Ensuring the fingernails are short could help prevent scratching the affected scalp, which could otherwise worsen atopic dermatitis. - Wear lightweight clothes
Thick clothes usually result in sweating, which triggers atopic dermatitis. Therefore, children should wear lightweight clothes to reduce sweating. - Play outdoors
Children should play outside in the sun to manage their condition. However, they must not stay in the sun for prolonged periods because excessive exposure may increase the risk of skin cancer. - Use a humidifier at home
Using a humidifier could help keep their skin moist at home. However, the humidity levels must be kept below 40%, as higher levels may promote the growth of dust mites. - Stay in a cool environment
An air conditioner or fan in the child’s room could help keep the space cool and avoid sweating. - Identify food allergens
Parents must identify food allergies that may cause atopic dermatitis and remove them from the child’s meal plan. This should be done simultaneously when the child receives skin inflammation treatment. Before making any alterations, one should also speak to an expert about a meal plan.

